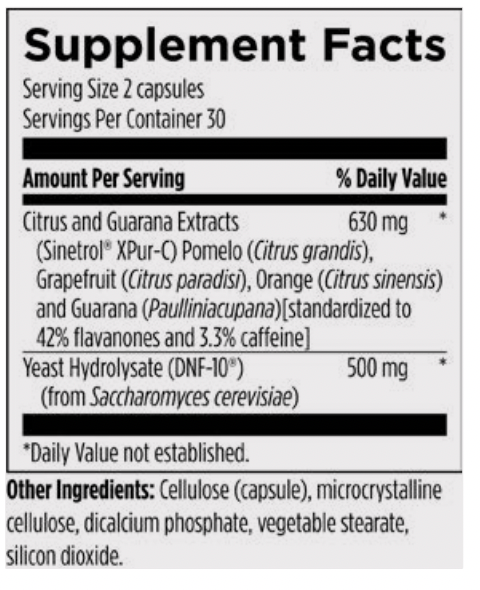
Metabolic Ignite
Key Ingredient: This is a gut peptide (DNF-10) that helps activate a reaction. Helps the body get into a fat burning state. DNF-10 acts on the gut-brain axis by regulating the mediators of appetite.
Works very well with the Metabolic Detox Shake. This was developed by Designs For Health as a natural alternative of peptides that you inject. Or you use this (with the shake) after your stop using things you inject.
These two products in combination help you control appetite, help you feel full and also feed your muscles. Maintaining muscle is a critical objective for all of us.
Take 30 minutes before a meal or shake.
==>>The two key ingredients in this product, Sinetrol® XPur‑C and
DNF‑10®, have complementary mechanisms of action.
Metabolic Ignite is a newly formulated product targeted to promote healthy body
composition, satiety, and increased basal metabolic rate (BMR).*
This clinically studied blend of citrus and guarana extracts alongside peptides from Saccharomyces cerevisiae helps support reductions in fat mass and waist/hip circumference.*
It is designed to support healthy weight management by helping to increase the body’s energy expenditure and satiety without causing the side effects associated with other weight reduction formulas.
Deep Dive Into The Science Of The Key Ingredients From Manufacturing Partner
DNF‑10® contains non‑pathogenic yeast hydrolysate (YH) peptides derived from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. YH peptides have a molecular weight <10KD and contain Cyclo(L‑histidyl‑L‑proline), a naturally occurring cyclic peptide resulting from
the formal condensation of both the amino and acid groups of L‑histidine with the acid and amino groups of L‑proline, which may be responsible for their potential to support healthy metabolism and satiety.
An animal study involving the administration of YH reported decreases in serum triglycerides and low‑density lipoprotein levels, alongside the inhibition
of hepatic glucose‑6‑phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) activity.9 Another animal study reported significantly lowered serum ghrelin levels in the presence of YH administration.2 Lowered ghrelin levels are associated with appetite
attenuation.
An animal study revealed that YH may help promote satiety through the reduction of neuropeptide Y expression in the hypothalamus.
An eight‑week randomized controlled trial involving 30 obese women investigated the effects of 500 mg daily supplementation with DNF‑10® .3 The participants were instructed to continue their regular diet and exercise regimen patterns the same as before.
At the study terminus, the treatment group experienced significant reductions in body fat and percent body fat of ‑4.6 lbs and ‑2.3%, respectively, compared to baseline, with no change in the control group.
In addition, parameters related to appetite were improved in the treatment group when compared to control. A reduction in the caloric intake in the intervention group was observed and reached ‑600 kcal/day by the end of the eight‑week study.
Conversely, the control group experienced a slight increase in caloric intake that fluctuated up to +200 kcal throughout the study. The control group desired food and thought about food more frequently than the treatment group.
Significant reductions in sweet preference were also reported in the treatment group; alternatively, the placebo group experienced a slight increase in sweet preference during the same time period.
A similar RCT involving obese men and women (ages 20 to 50 years) were randomized to receive 0.5g DNF‑10® twice per day, 30 minutes before breakfast and dinner for 10 weeks, or placebo, and were instructed to continue their regular diet and exercise regimen patterns the same as before.
Significant differences in abdominal fat thickness, abdominal fat area,
and abdominal circumference between the treatment and placebo groups were observed at the study terminus.
The DNF‑10® supplemented group lost 5.7 pounds after 10 weeks with no significant change in lean mass. This fat loss may be attributed, at least in part, to reduced appetite responsible for a decline in caloric intake up to ‑392.3 kcal/day.
Two additional clinical studies assessed the effects of supplementing women with 1 g of DNF‑10® per day and demonstrated similar significant reductions in body weight and fat mass.
In conclusion, supplementation with DNF‑10® may help support a normal appetite and healthy body composition, especially when combined with a healthy diet and exercise.*
The two key ingredients in this product, Sinetrol® XPur‑C and
DNF‑10®, have complementary mechanisms of action.
For example, based on study results, they may support a significant
daily caloric deficit, such as 180 kcal due to a REE increased by Sinetrol® XPur‑C , and 400 to 600 fewer ingested kcal due to diminished hunger by DNF‑10®.* This may result in a total deficit of 580 to 780 kcal/day or 4,060 to 5,460 Kcal/
week, which is equivalent to 1.1 to 1.5 lbs of fat/week.*
Citrus fruits contain many bioactive constituents that support healthy metabolism and
optimal cellular functioning.1 Sinetrol® XPur‑C contains extracts from grapefruit, three
varieties of orange, and guarana that contain flavonoids such as anthocyanins, phenolic
acids, and the flavanones naringin and hesperidin.1
Biochemically, Sinetrol® XPur and its concentrated version, Sinetrol® XPur‑C, supports
body fat metabolism through its ability to promote antioxidative status, a normal
inflammatory response, and healthy lipid metabolism.1 A clinical study with Sinetrol®
XPur‑C was shown to help activate cyclic AMP‑dependent uncoupling protein‑2 and
help inhibit cAMP‑phosphodiesterase (PDE), which results in increased lipolysis
(release of free fatty acids from adipocytes), thermogenesis, and basal metabolic rate.
One double‑blind placebo‑controlled study supplemented 77 subjects with 450 mg
Sinetrol® XPur, twice daily, for 16 weeks. The results showed a statistically significant
increase in resting energy expenditure (REE) of 181 kcal/day in the intervention group,
with no significant change in the control group (University of Murcia, Spain; submitted
for publication).
In laboratory studies, citrus flavonoids have been shown to suppress atherogenesis,
inhibit fatty acid and triglyceride synthesis, and increase fatty acid oxidation, demonstrating their potential antiadipogenic and antiatherogenic properties. In animal and experimental models of obesity and hyperlipidemia, plasma lipid and cholesterol levels were observed to improve significantly in the presence of naringin, a flavanone found in citrus fruits.